Ergonomic Resources
Useful reference material for Ergonomics.
Why monitor mounts

- Reduced footprint = Maximised office space
- More desks on more floors = Less personal space and less desk space
- 25% saving in desk space with more usable capacity
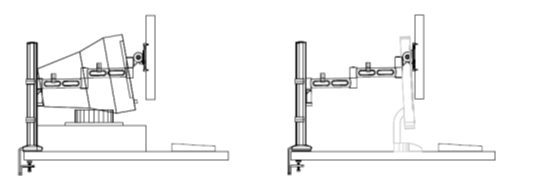
- Productivity gains

- According to a study by the NY Times, by using monitor mounts, user productivity could increase up to 44%. Other studies suggest even higher.
Reference – Monitor mounts give significant ergonomic benefits. Washington State Department ROI delivered within 2 months.
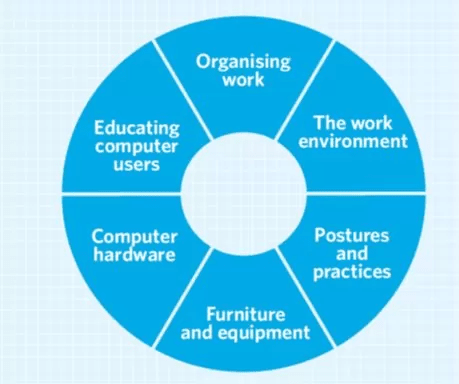
Ergonomic tips for the workplace
Tips for setting up your workstation
Managing the environment - factors to consider when using computers
Productivity gain using dual monitors
- According to JPR (Jon Peddie Research) – as reported by New York Times. Adding a monitor can boost productivity by 20%-30%. Key findings of the research.
- Almost everyone participated in the research agrees by having multiple display units would increase the productivity of the work they perform.
- Productivity estimations average to 42% improvement.
Ergonomic definitions and terminology


Terminology 
- Ergonomics – The science of work. Ergonomics removes barriers to quality, productivity, and safe human performance by fitting products, tasks and environments to people.
- Ergonomic program – A systematic process for anticipating, identifying, analyzing and controlling ergonomic risk factors.
- Administrative Control – Procedures and methods, set up by the employer, that significantly reduce exposure to risk factors by altering the way in which work is performed; examples include employee rotation, job task enlargement, and adjustment of work pace.
- Anthropometry – Anthropometry is the branch of the human sciences that deals with body measurements.
- Awkward Posture -Posture is the position of the body while performing work activities. Awkward posture is associated with an increased risk for injury. It is generally considered that the more a joint deviates from the neutral (natural) position, the greater the risk of injury.
- Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs) – Term used for injuries that occur over a period because of repeated trauma or exposure to a specific body part, such as the back, hand, wrist and forearm. Muscles and joints are stressed, tendons are inflamed, nerves pinched or the flow of blood is restricted. Common occupational induced disorders in this class include carpal tunnel syndrome, epicondylitis (tennis elbow), tendinitis, tenosynovitis, synovitis, stenosing tenosynovitis of the finger, DeQuervian’s Syndrome, and low back pain.
- Engineering Control – Physical changes to jobs that control exposure to risk. Engineering controls act on the source of the hazard and control employee exposure to the hazard without relying on the employee to take self-protective action or intervention. Examples include: changing the handle angle of a tool, using a lighter weight part, and providing a chair that has adjustability.
Reference and acknowledgement, Ergoweb LLC.
Ergonomics design and reference guide
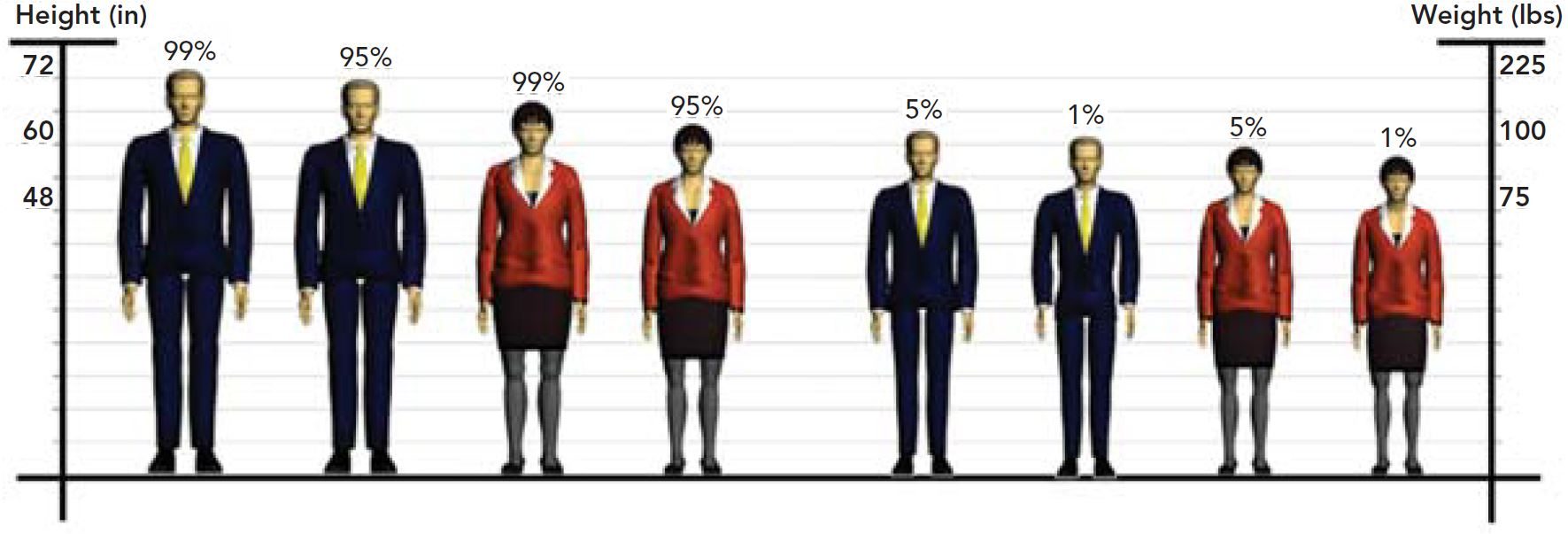
Study completed by Allsteel – Considerations that designers take when making sure their product is suitable for the human body.
For the full Allsteel study, download the pdf here: Ergonomics Design and Reference Guide Whitepaper
Study involves following areas:
- Anthropometric Measurements
- Common Workplace Postures
- Common Workplace Motions
- Office Furniture Guidelines for Fit and Function
- Universal Design Considerations
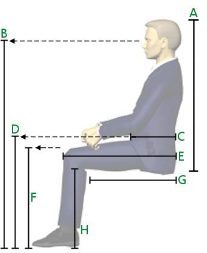


Reference and acknowledgement – Allsteel Inc. Muscatine, Iowa 52761-5257